Microsoft Exchange Server is a powerful suite of communication and collaboration tools that enables businesses to manage email, calendars, contacts, and more. Designed for both on-premises and cloud deployments, Exchange Server offers a robust platform for secure and reliable communication, fostering enhanced productivity and collaboration within organizations.
From its core functionalities like email, calendar, and contact management, Exchange Server extends its capabilities to encompass features like shared calendars, mailboxes, and advanced security measures. It integrates seamlessly with other Microsoft products like Microsoft 365, Azure, and Active Directory, further enriching its versatility and providing a comprehensive solution for modern business needs.
Introduction to Microsoft Exchange Server
Microsoft Exchange Server is a powerful messaging and collaboration platform that provides a comprehensive suite of tools for managing email, calendars, contacts, and other communication services. It is designed to meet the needs of businesses of all sizes, from small startups to large enterprises.
Exchange Server offers a wide range of features and functionalities that enhance communication and collaboration within organizations. These features include:
Core Functionalities of Microsoft Exchange Server
- Email Management: Exchange Server provides robust email management capabilities, including email storage, delivery, and security. It enables users to send and receive emails, manage their inboxes, and collaborate on email projects.
- Calendar and Scheduling: Exchange Server facilitates calendar sharing and scheduling, allowing users to view and manage their schedules, book meetings, and send meeting invitations.
- Contact Management: Exchange Server provides a central repository for managing contacts, enabling users to store and organize contact information, share contact lists, and easily communicate with colleagues and clients.
- Collaboration Tools: Exchange Server offers a range of collaboration tools, including shared calendars, shared mailboxes, and public folders, enabling teams to work together effectively.
- Security and Compliance: Exchange Server prioritizes security and compliance, providing features such as spam filtering, anti-malware protection, data encryption, and message retention policies.
Purpose and Benefits of Using Exchange Server
Exchange Server is designed to streamline communication and collaboration within organizations, offering numerous benefits:
- Improved Communication: Exchange Server provides a centralized platform for email, calendars, and contacts, enabling seamless communication and collaboration among users.
- Enhanced Productivity: By simplifying communication and scheduling, Exchange Server helps users stay organized and focused, increasing their productivity.
- Increased Collaboration: Exchange Server’s collaboration tools, such as shared calendars and mailboxes, facilitate teamwork and improve project outcomes.
- Enhanced Security: Exchange Server’s security features protect against spam, malware, and unauthorized access, ensuring data confidentiality and integrity.
- Simplified Management: Exchange Server offers a centralized administration console, simplifying the management of email, calendars, and other communication services.
Target Audience and Use Cases for Exchange Server
Exchange Server is a versatile platform suitable for various organizations and use cases:
- Businesses of All Sizes: Exchange Server caters to businesses of all sizes, from small startups to large enterprises, offering scalable solutions to meet their communication and collaboration needs.
- Education Institutions: Schools, colleges, and universities can leverage Exchange Server for student and faculty email, calendar management, and online collaboration tools.
- Government Agencies: Government agencies can use Exchange Server for secure communication, email archiving, and compliance with regulatory requirements.
- Healthcare Organizations: Hospitals, clinics, and other healthcare providers can use Exchange Server for patient communication, appointment scheduling, and secure data sharing.
- Non-Profit Organizations: Non-profit organizations can utilize Exchange Server for donor communication, event planning, and volunteer coordination.
Key Features and Capabilities
Microsoft Exchange Server is a comprehensive platform that offers a wide range of features for managing email, calendars, contacts, and collaboration. It is designed to enhance productivity and streamline communication within organizations.
Email Management
Email management is a core function of Exchange Server. It provides robust capabilities for sending, receiving, and managing emails.
- Message Routing and Delivery: Exchange Server handles the routing and delivery of emails, ensuring reliable and efficient communication. It uses a sophisticated routing system to direct emails to the correct recipients, even if they are located in different locations or on different networks.
- Email Security: Exchange Server incorporates advanced security features to protect emails from spam, viruses, and other threats. It utilizes spam filtering, anti-virus scanning, and data loss prevention (DLP) mechanisms to ensure the integrity and confidentiality of email communications.
- Email Archiving: Exchange Server allows for email archiving, which enables organizations to store and retrieve emails for compliance and regulatory purposes. It provides a secure and searchable repository for historical email data, making it easier to access and manage information over time.
Calendar Management
Exchange Server offers powerful calendar management features that help users schedule appointments, meetings, and events efficiently.
- Appointment Scheduling: Users can easily schedule appointments, set reminders, and invite attendees. Exchange Server synchronizes calendars across devices, ensuring that users always have access to their schedules.
- Meeting Scheduling: Exchange Server simplifies meeting scheduling by allowing users to create meetings, invite attendees, and manage conflicts. It provides features for setting meeting times, locations, and agendas, and for sending out meeting requests and confirmations.
- Calendar Sharing: Users can share their calendars with colleagues, supervisors, or other authorized individuals, enabling them to view schedules and availability. This promotes transparency and facilitates collaboration.
Contact Management
Exchange Server provides a centralized platform for managing contacts, making it easy to store, organize, and share contact information.
- Contact Storage and Organization: Exchange Server offers a robust contact database where users can store contact information, including names, addresses, phone numbers, email addresses, and other relevant details. It allows users to organize contacts into groups or categories for easy retrieval.
- Contact Sharing: Users can share their contact lists with other users or groups, promoting collaboration and efficient communication. This allows team members to access and utilize contact information without having to manually create duplicates.
- Contact Synchronization: Exchange Server synchronizes contacts across devices, ensuring that users always have access to their contact information, regardless of the device they are using.
Collaboration Tools
Exchange Server offers various collaboration tools that enable users to work together seamlessly.
- Shared Calendars: Users can share calendars with colleagues or teams, allowing them to view each other’s schedules and coordinate appointments and meetings. This promotes transparency and efficient scheduling.
- Shared Mailboxes: Exchange Server allows organizations to create shared mailboxes that can be accessed by multiple users. This is useful for managing email communications for teams, departments, or specific projects.
- Public Folders: Exchange Server supports public folders, which provide a shared space for storing documents, files, and other information. Users can access and contribute to public folders, facilitating collaboration and knowledge sharing.
Security and Compliance Features
Exchange Server is designed with robust security and compliance features to protect sensitive data and meet regulatory requirements.
- Data Encryption: Exchange Server encrypts email messages and other data in transit and at rest, protecting information from unauthorized access. It uses industry-standard encryption protocols to ensure the confidentiality and integrity of data.
- Access Control: Exchange Server allows administrators to control user access to email, calendars, contacts, and other features. It provides granular permissions to ensure that only authorized users can access sensitive information.
- Compliance Features: Exchange Server includes features that help organizations meet compliance requirements, such as data retention policies, legal hold capabilities, and eDiscovery tools. It enables organizations to preserve and manage data for legal or regulatory purposes.
Architecture and Deployment Options: Microsoft Exchange Server
Microsoft Exchange Server offers various deployment models to cater to different organizational needs and infrastructure preferences. Understanding these options is crucial for selecting the most suitable approach for your specific requirements.
Deployment Models
The deployment model determines the physical location and management of your Exchange Server environment. There are three primary options:
- On-premises: This model involves installing and managing Exchange Server on your own physical hardware within your organization’s data center. You have complete control over the infrastructure and its configuration.
- Cloud: In this model, Exchange Server is hosted by a third-party provider in their data center, such as Microsoft Azure. This eliminates the need for on-site hardware and management, making it a cost-effective option.
- Hybrid: This model combines elements of both on-premises and cloud deployments. Some Exchange Server components are hosted on-premises, while others are hosted in the cloud. This allows organizations to gradually transition to the cloud or leverage the benefits of both models.
Components of an Exchange Server Environment, Microsoft exchange server
An Exchange Server environment consists of several key components that work together to provide email, calendar, and other collaboration services:
- Client Access Server (CAS): This component acts as the gateway for client connections, handling tasks like authentication, message routing, and providing access to the mailbox database.
- Mailbox Server: This component stores user mailboxes and associated data, including emails, calendar entries, and contacts.
- Edge Transport Server: This optional component acts as a perimeter server, providing security and spam filtering for incoming and outgoing messages.
- Unified Messaging (UM) Server: This component enables users to access voicemail messages through email, mobile devices, or other channels.
- Directory Services: Active Directory (AD) is used to manage user accounts, permissions, and other organizational information.
Hardware and Software Requirements
The hardware and software requirements for deploying Exchange Server vary depending on the chosen deployment model, the number of users, and the expected workload.
- Hardware: On-premises deployments require dedicated servers with sufficient processing power, memory, and storage capacity. Cloud deployments typically involve virtualized environments, where the hardware is managed by the cloud provider.
- Software: Exchange Server requires a compatible operating system, such as Windows Server, and specific software components, such as the .NET Framework and SQL Server.
User Management and Administration
Managing user accounts and their access to Exchange Server resources is a crucial aspect of Exchange Server administration. This involves creating and managing user accounts, setting up security policies, and monitoring user activities.
Creating and Managing User Accounts
Creating and managing user accounts involves a series of steps to ensure users have the necessary access to Exchange Server resources.
- Creating User Accounts: Exchange Server provides a graphical user interface (GUI) for creating user accounts. The process typically involves entering the user’s name, email address, and password. You can also configure other settings, such as the user’s mailbox size, default calendar settings, and access permissions.
- Managing User Accounts: After creating user accounts, administrators can modify user account settings, such as changing passwords, updating contact information, and managing mailbox quotas. The GUI offers a centralized platform for managing user accounts and their associated settings.
Role-Based Access Control
Exchange Server implements a robust role-based access control (RBAC) system to enhance security. This system assigns specific roles to users, granting them access to resources based on their assigned roles.
- Role Assignment: Administrators define roles and assign them to users. Each role defines specific permissions for accessing and managing Exchange Server resources. For instance, a “Help Desk” role might have limited access to user mailboxes for troubleshooting purposes, while a “Manager” role might have broader access to manage users within a department.
- Role-Based Permissions: RBAC allows administrators to control user access to specific features, such as sending and receiving emails, accessing public folders, and managing calendars. This fine-grained control helps prevent unauthorized access and ensures data security.
Managing Exchange Server
Exchange Server offers a variety of tools and methods for managing its functionality and ensuring optimal performance.
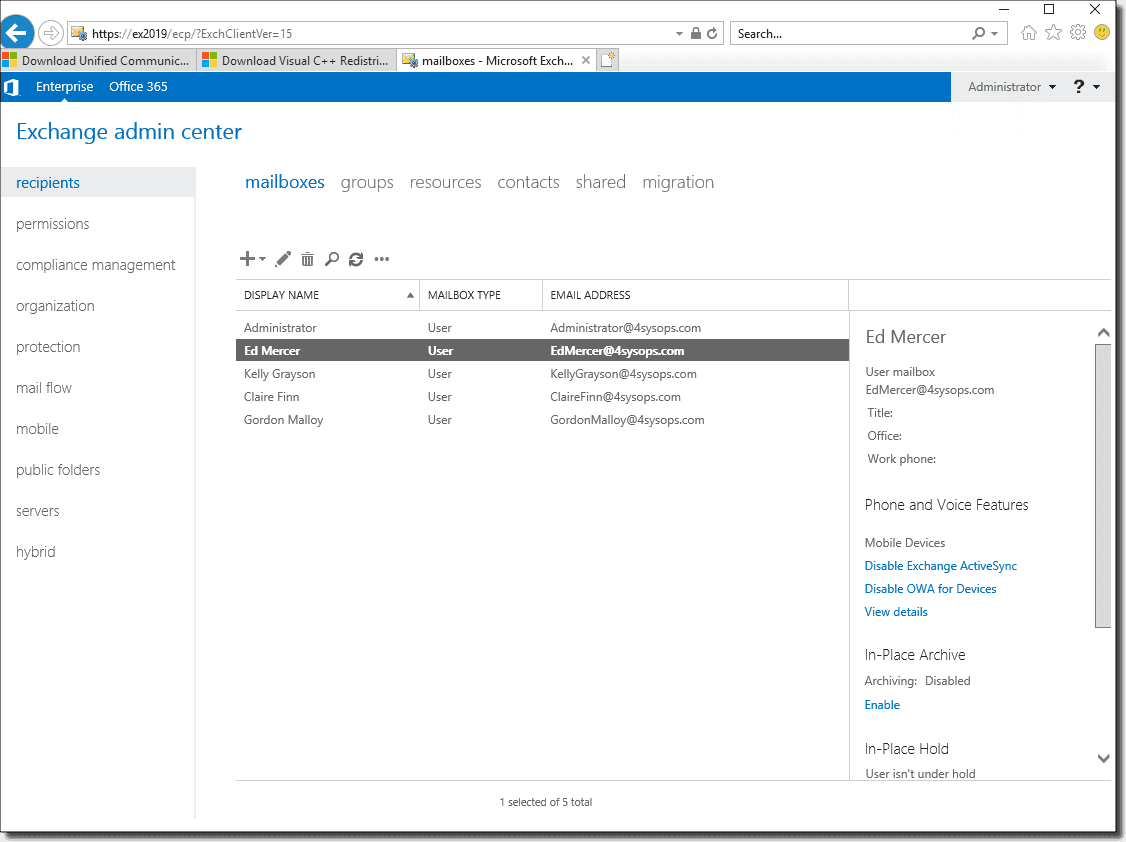
- Exchange Admin Center (EAC): The EAC is a web-based interface for managing Exchange Server. It provides a centralized platform for managing user accounts, mailboxes, and other server settings. The EAC offers a user-friendly interface for navigating various administrative tasks.
- Exchange Management Shell (EMS): The EMS is a command-line interface for managing Exchange Server. It provides advanced features and allows administrators to automate repetitive tasks. The EMS is a powerful tool for experienced administrators who prefer a command-line approach.
Email Security and Compliance
Microsoft Exchange Server prioritizes email security and compliance to protect sensitive data and meet regulatory requirements. It incorporates robust features to safeguard against spam, malware, and data breaches, ensuring business continuity and user privacy.
Spam Filtering and Malware Protection
Exchange Server employs advanced spam filtering techniques to identify and block unsolicited emails, minimizing the risk of phishing attacks and malicious content reaching users’ inboxes. It utilizes multiple layers of protection, including:
- Content filtering: Analyzing email content for suspicious patterns, s, and known spam indicators.
- Sender reputation: Evaluating the sender’s reputation based on blacklists and other intelligence sources.
- Real-time protection: Utilizing cloud-based services and machine learning to detect emerging threats and spam tactics.
Malware protection safeguards against harmful attachments and links by scanning emails for viruses, Trojans, and other malicious code. It integrates with antivirus engines and sandboxing technologies to isolate and neutralize threats before they can reach users’ devices.
Data Loss Prevention (DLP) and Encryption
Exchange Server provides comprehensive data loss prevention (DLP) capabilities to protect sensitive information from unauthorized disclosure. It allows administrators to define policies that identify and control the flow of sensitive data, such as credit card numbers, social security numbers, and confidential documents.
- Policy-based controls: Implementing rules to block or restrict the sending or receiving of sensitive data based on content, sender, or recipient.
- Real-time monitoring: Tracking and reporting on potential data leaks and violations.
- Data redaction: Removing sensitive information from emails before they are sent.
Data encryption protects email content during transmission and storage. Exchange Server supports various encryption protocols, including Transport Layer Security (TLS) and Secure/Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions (S/MIME), ensuring confidentiality and integrity of communications.
Compliance with Industry Regulations
Exchange Server helps organizations meet compliance requirements for various industry regulations, including:
- General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR): Providing features for data subject access requests, data portability, and data erasure, enabling compliance with GDPR principles.
- Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA): Offering encryption, access controls, and audit trails to protect patient health information (PHI) and comply with HIPAA regulations.
Integration with Other Microsoft Products

Exchange Server seamlessly integrates with other Microsoft products, creating a unified and collaborative ecosystem for businesses. This integration streamlines workflows, enhances productivity, and provides a consistent user experience across various applications.
Integration with Microsoft 365
Microsoft 365 is a cloud-based subscription service that includes a suite of productivity applications, including Exchange Online. Exchange Server integrates with Microsoft 365, allowing businesses to leverage the benefits of both on-premises and cloud solutions.
- Hybrid Deployment: Exchange Server can be deployed in a hybrid configuration, where some mailboxes are hosted on-premises and others are hosted in the cloud on Exchange Online. This approach allows businesses to gradually transition to the cloud or to maintain on-premises control over sensitive data while leveraging the benefits of cloud services.
- Coexistence: Exchange Server can coexist with Exchange Online, enabling businesses to manage both on-premises and cloud mailboxes from a single console. This approach provides flexibility and allows businesses to gradually migrate their infrastructure to the cloud.
- Unified Messaging: Exchange Server integrates with Microsoft Teams, providing a unified messaging platform that combines email, voice, video, and instant messaging. This integration enhances communication and collaboration within organizations.
Integration with Azure
Microsoft Azure is a cloud computing platform that provides a wide range of services, including infrastructure, storage, and networking. Exchange Server can leverage Azure services to enhance its functionality and scalability.
- Azure Active Directory: Exchange Server can integrate with Azure Active Directory (Azure AD), providing a centralized identity management system for users and devices. This integration enables single sign-on (SSO) and simplifies user management across different applications.
- Azure Backup: Exchange Server can be backed up to Azure, providing a reliable and secure off-site backup solution. This integration ensures data protection and disaster recovery capabilities.
- Azure Virtual Machines: Exchange Server can be deployed on Azure Virtual Machines (VMs), providing a flexible and scalable infrastructure. This approach allows businesses to quickly provision and scale their Exchange environment based on their needs.
Integration with Active Directory
Active Directory (AD) is a directory service that provides a centralized management system for users, computers, and other resources within a network. Exchange Server tightly integrates with Active Directory, leveraging its features for user management, authentication, and authorization.
- User Management: Exchange Server uses Active Directory to manage user accounts, permissions, and group memberships. This integration simplifies user management and ensures consistency across the network.
- Authentication: Exchange Server uses Active Directory for user authentication, ensuring that only authorized users can access email and other services. This integration enhances security and prevents unauthorized access.
- Authorization: Exchange Server uses Active Directory to control user access to specific mailboxes, folders, and other resources. This integration allows businesses to implement granular access control policies and prevent data breaches.
Migration and Upgrade Considerations
Moving to a new version of Exchange Server or migrating from an older system involves careful planning and execution to ensure a smooth transition and minimal disruption to your email services. This section will Artikel the steps involved in migrating from older versions of Exchange and upgrading to the latest version.
Migration from Older Versions of Exchange
Migrating from older versions of Exchange involves moving mailboxes, data, and configurations to a newer Exchange environment. The process can be complex, depending on the source version, the target version, and the size of your organization.
- Assess your current environment: Before starting the migration, it is crucial to assess your current Exchange environment, including the version, size, and configuration of your mailboxes, servers, and network infrastructure. This assessment will help you identify potential challenges and plan accordingly.
- Choose a migration method: There are various migration methods available, including cutover migration, staged migration, and hybrid migration. The choice of method depends on your specific needs and the size of your organization. A cutover migration involves migrating all mailboxes at once, while a staged migration allows you to migrate mailboxes in batches. A hybrid migration allows you to gradually move mailboxes to the cloud while keeping some on-premises.
- Prepare the target environment: Once you have chosen a migration method, you need to prepare the target Exchange environment, including installing the necessary software, configuring the server, and creating user accounts. This preparation should be done before starting the actual migration process.
- Migrate mailboxes and data: The next step involves migrating mailboxes and data from the source environment to the target environment. This can be done using tools like the Exchange Server Migration Wizard or third-party migration tools. It is important to test the migration process thoroughly before moving all mailboxes.
- Verify and validate: After the migration is complete, it is crucial to verify and validate the new environment to ensure that all mailboxes and data have been migrated successfully. This includes checking email functionality, user access, and data integrity.
Upgrade to the Latest Version of Exchange
Upgrading to the latest version of Exchange Server involves updating your existing Exchange environment to take advantage of the new features, security enhancements, and performance improvements. The upgrade process can be straightforward or complex, depending on the current version and the target version.
- Check compatibility: Before upgrading, it is essential to check the compatibility of your existing hardware and software with the latest version of Exchange. This includes checking the operating system, databases, and other components.
- Plan and prepare: Planning and preparation are crucial for a successful upgrade. This includes identifying the upgrade path, backing up your existing environment, and creating a test environment for testing the upgrade process.
- Perform the upgrade: Once you have planned and prepared, you can proceed with the upgrade process. This involves running the setup program and following the on-screen instructions. It is important to follow the recommended best practices and documentation provided by Microsoft.
- Test and validate: After the upgrade is complete, it is crucial to test and validate the new environment to ensure that all services are working correctly. This includes checking email functionality, user access, and data integrity.
- Document the upgrade: Documenting the upgrade process is essential for future reference and troubleshooting. This includes recording the steps taken, any issues encountered, and the solutions implemented.
Planning and Executing a Successful Migration
A successful migration or upgrade requires careful planning and execution. Here are some key considerations:
- Define your goals and objectives: Clearly define the goals and objectives of the migration or upgrade. What are you trying to achieve? What are the expected benefits? Having a clear understanding of your goals will help you plan effectively.
- Assess your current environment: Thoroughly assess your current Exchange environment, including the version, size, configuration, and dependencies. This will help you identify potential challenges and plan accordingly.
- Choose the right migration method: Select a migration method that best suits your needs and the size of your organization. Consider factors such as the number of mailboxes, the complexity of your environment, and the desired downtime.
- Prepare the target environment: Ensure that the target environment is properly configured and ready to receive the migrated data. This includes installing the necessary software, creating user accounts, and configuring security settings.
- Test the migration process: Test the migration process thoroughly before migrating all mailboxes. This will help identify and resolve any issues before they impact production.
- Communicate with users: Keep users informed about the migration process and any potential disruptions. Provide clear instructions and support to minimize user impact.
- Monitor and validate: Monitor the migration process closely and validate the new environment after the migration is complete. Ensure that all mailboxes and data have been migrated successfully and that all services are working correctly.
Troubleshooting and Support

Like any complex software system, Exchange Server can experience issues. Fortunately, Microsoft provides various tools and resources to help you troubleshoot and resolve problems. Understanding common issues, available support options, and Microsoft’s role in resolving issues is crucial for maintaining a smooth and efficient Exchange environment.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting Techniques
Common Exchange Server issues can be categorized into several areas:
- Email Delivery Problems: These include issues like emails not being sent, received, or stuck in the queue. Troubleshooting techniques involve checking mail flow rules, verifying sender and recipient addresses, examining the message queue, and ensuring the Exchange server is connected to the internet.
- User Access and Authentication Issues: Problems accessing mailboxes, calendars, or other Exchange features can arise from incorrect passwords, account lockouts, or issues with Active Directory integration. Troubleshooting involves verifying user credentials, checking Active Directory synchronization, and reviewing user permissions.
- Performance and Availability Issues: Slow email delivery, high server load, or unexpected outages can indicate performance or availability issues. Troubleshooting involves monitoring server resources, analyzing logs, identifying potential bottlenecks, and checking for hardware failures.
- Security and Compliance Issues: Exchange Server plays a crucial role in securing sensitive information. Issues like spam filtering failures, data breaches, or non-compliance with regulations require careful troubleshooting. This involves reviewing security settings, analyzing logs, and implementing appropriate security measures.
Available Resources for Support and Documentation
Microsoft offers comprehensive resources to assist administrators in troubleshooting and resolving Exchange Server issues:
- Microsoft Exchange Server Documentation: The official Microsoft documentation provides detailed information about Exchange Server features, configuration, and troubleshooting. This is an excellent starting point for understanding how Exchange works and addressing common problems.
- Microsoft TechNet: TechNet offers a vast collection of articles, tutorials, and forums dedicated to Exchange Server. You can find solutions to specific issues, learn best practices, and engage with other Exchange administrators.
- Microsoft Learn: Microsoft Learn provides online courses and training materials to enhance your Exchange Server knowledge. You can learn about various aspects of Exchange administration, including troubleshooting, security, and best practices.
- Microsoft Support Forums: Microsoft Support Forums offer a platform to connect with other Exchange administrators and Microsoft engineers. You can post questions, share experiences, and seek assistance from the community.
Role of Microsoft Support Services
For critical issues that require expert assistance, Microsoft offers various support services:
- Microsoft Premier Support: This premium support service provides direct access to Microsoft engineers for proactive guidance, technical support, and issue resolution. It is ideal for organizations that require rapid response times and customized solutions.
- Microsoft Online Support: Microsoft Online Support offers various options, including knowledge base articles, online troubleshooting tools, and direct contact with Microsoft support agents. This is a good option for organizations that need immediate assistance but may not require the full scope of Premier Support.
Future Trends and Innovations
Microsoft Exchange Server has been a cornerstone of email communication and collaboration for businesses of all sizes for decades. As technology continues to evolve, Exchange Server is also adapting and innovating to meet the demands of a rapidly changing digital landscape.
Impact of Cloud Computing and Mobile Technologies
The rise of cloud computing and mobile technologies has profoundly impacted the way businesses communicate and collaborate. Exchange Server has embraced these trends, offering flexible deployment options and enhanced mobile capabilities.
- Hybrid Deployments: Exchange Server supports hybrid deployments, allowing organizations to leverage the benefits of both on-premises and cloud-based solutions. This flexibility enables organizations to gradually transition to the cloud at their own pace, minimizing disruption and maximizing control over their data.
- Mobile Access: Exchange Server provides seamless mobile access to email, calendar, and contacts, empowering users to stay connected and productive from anywhere. Mobile devices can synchronize data with Exchange Server, ensuring consistency and accessibility across platforms.
- Cloud-Based Services: Microsoft offers cloud-based email and collaboration services like Microsoft 365, which leverage Exchange Server technology. These services provide a fully managed solution, eliminating the need for on-premises infrastructure and simplifying administration.
Emerging Features and Advancements
Exchange Server continues to evolve, incorporating cutting-edge features and advancements to enhance user experience and security.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI is being integrated into Exchange Server to enhance spam filtering, automate tasks, and provide personalized experiences. For instance, AI-powered spam filters can analyze email content and sender behavior to identify and block malicious emails with greater accuracy.
- Unified Communications: Exchange Server is becoming increasingly integrated with other communication tools, such as instant messaging and video conferencing. This trend enables organizations to provide a unified communication platform, streamlining collaboration and communication across different channels.
- Enhanced Security: Exchange Server is constantly evolving to address emerging security threats. Features like advanced threat protection, data loss prevention, and multi-factor authentication help organizations safeguard their data and protect their users from malicious attacks.
Last Word
Understanding the nuances of Microsoft Exchange Server is crucial for businesses seeking to optimize their communication and collaboration processes. By leveraging its capabilities, organizations can streamline operations, enhance security, and ensure seamless communication across diverse platforms. As technology evolves, Exchange Server continues to adapt, offering innovative solutions that empower businesses to thrive in the digital age.
Microsoft Exchange Server is a powerful tool for managing email, calendars, and contacts. It can be a bit complex to set up, but once you have it running, it’s a great way to keep your business organized. Of course, you need a place to relax and de-stress after dealing with all that technical stuff.
Building your own DIY raised garden beds is a fantastic way to unwind and connect with nature. And once you’ve got your garden thriving, you can use Exchange Server to send out invitations to your friends and family for a relaxing afternoon amongst the flowers and vegetables.